Emotions are complicated, and it is often hard to pinpoint what exactly you are going through. You may sometimes find it challenging to express your feelings when you aren’t sure what words describe them the best. Stress and anxiety, along with worry, are among the most confusing terms today. This is because of lax usage and because the difference between stress and anxiety is very subtle and needs to be clarified.
To understand the differences between stress and anxiety, let us first examine what the two conditions involve. This includes any sub categories or types of emotions falling under the two as recognized in clinical psychology.
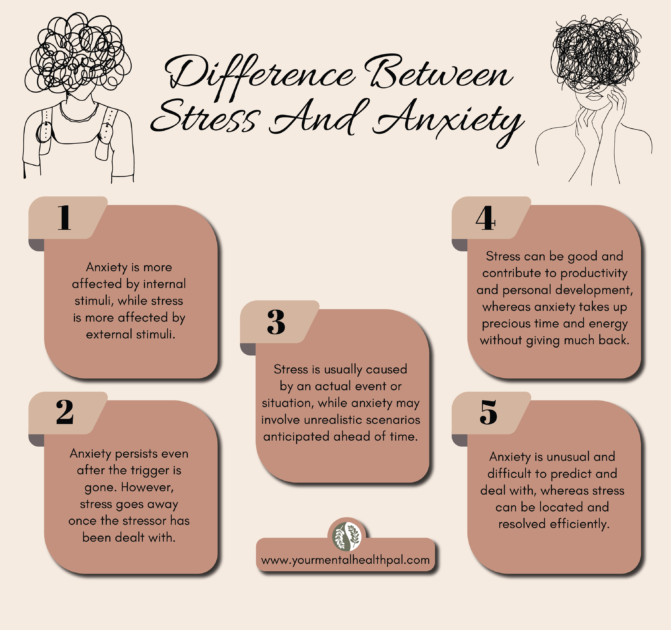
What is the difference between stress and anxiety in Psychology?
Anxiety is an emotion that may cause worried thoughts, feelings of tension, and physical symptoms like high blood pressure. For instance, they might think they may be fired for having some fun or the job or that people might stop talking to them after a minor humiliation or a mistake is pointed out.
Symptoms of Anxiety as per the DSM-V
-Restlessness or being on edge
-Dizziness and Fatigue
-Difficulty concentrating or mind going blank.
-Irritability.
-Muscle tension.
-Difficulty falling or staying asleep, or restless unsatisfying sleep
Stress is a feeling of physical or emotional conflict – or tension. It is caused by a conflict or dissonance and can be dealt with by removing it. As stated earlier, you can also note that anxiety causes tension, while stress is this feeling of pressure itself.
Symptoms of acute stress, according to the DSM-V
-Emotional Ups and Downs
-Chest pain or a feeling like your heart is racing.
-Exhaustion or trouble sleeping(insomnia, sleep deprivation)
-Headaches and dizziness
-Poor concentration and irritability
-Wanting to be alone
-Muscle tension
-Jaw clenching.
-Digestive problems.
Stress vs. Anxiety: Are stress and anxiety the same thing?
Comparing and contrasting the two based on the symptoms shows that stress and anxiety are similar but not the same. You can understand your situation better and identify the difference between stress and anxiety by asking these questions:-
-What is your condition caused by? Anxiety is caused by an imaginary event or situation, while stress is caused by a present or anticipated one.
-How easy is it to identify the cause? You can almost always locate the cause of stress, while anxiety may sometimes feel like it grabs you out of nowhere. For instance, you may be stressed about a work assessment being shifted earlier than it was supposed to be but may develop anxiety even if there was no such event about to occur.
-Is the cause internal or external? Anxiety is usually caused by internal processes, while stress is a response to external events. The symptoms of stress will go away after the stressor, either in the form of a situation or psychological trauma memory, is over, but anxiety persists over time.
-Is your condition beneficial or reality-based in some way? Stress can be good and even helpful when you need to perform well. On the other hand, anxious thoughts are usually intrusive and imaginative and eat away at your time and energy through a negative inner monologue.
-Does the cause of your condition seem unusual? Stress only happens or arises from certain events or stimuli you may get from the external world, while anxiety is a little more complicated. It can also be seen as being more sensitive to external stimuli and having harmful internal feelings based on them.
How to deal with stress, anxiety, and worry? Stress Vs. Anxiety
Now you have identified the difference between stress and anxiety. What to do next?
Since these conditions are similar despite the stress and anxiety difference, the same treatments, habits, and precautions are effective. Before we look at your next course of action, let us see the conditions related to anxiety and stress in the DSM-V:
Many mental health conditions related to stress exist, but among them, the most important ones are:-
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder(PTSD)
PTSD is a condition everyone’s heard of and understands the basics of. It is caused by an abnormally traumatic life event(can be childhood trauma) or situation and may take years to a lifetime to recover from. It is a part of Trauma & Stressor related disorders in the DSM-V.
Acute Stress Disorder
This disorder develops following a significant change or traumatic life event. It can be efficiently dealt with if you have a robust support system and good mental health with the help of a few or more therapy sessions.
Acute stress is the stress we usually experience. It is not as severe as the disorder of the same name. This good stress helps you mentally prepare for or cope with an unexpected or critical situation.
Anxiety comes in many shapes and forms. Here are some more prevalent anxiety disorder types and how they function:-
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
A condition where you are not stressed about something in particular but tend to worry about different conditions over time.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder(OCD)
Simply put, OCD is a combination of excessive thoughts and repetitive behaviors. The compulsions in OCD exist to cope with and resolve anxiety caused by this disorder.
Social Anxiety Disorder
Social anxiety disorder is anxiety toward being social, in the public eye, or the limelight. It involves fear and avoidance of people.
Panic Disorder
This disorder involves panic attacks or fear for no reason. It is not to be confused with panic attacks.
These conditions further highlight the subtle but existing difference between stress and anxiety. Both of these conditions can feel the same and may have similar causes or origins in some cases. You can also find that stress, anxiety, or any other similar conditions benefit from the same practices. On that note, the following is a list of possible short-term mental health goals you can start working on right now to cope with both conditions better.
How to get help with stress, anxiety, or anything related? Stress Vs. Anxiety
-Use the practice of mindfulness
Being in the moment can help you better cope with stress and anxiety. You can directly face the cause of your stress and engage in sensory stimuli to reduce the amount of attention given to anxiety. This might help calm your mind instantly in certain situations, especially if combined with focus on your breath.
-Exercise, eat more consciously and take a power nap if you find it helpful
Exercise is a habit known to have proven health benefits for many mental conditions and to improve your overall state of mind. There are various anxiety-reducing exercises that boost your mental health.
Eating consciously, like mindful eating exercise, can help boost your immunity and divert attention toward your senses.
Napping is a helpful activity that can restore your sleep schedule to what it was before anxiety and stress started draining your emotional energy.
-Try your hand at journaling
Journaling has many benefits, especially if you want to get to know yourself better, increase emotional awareness, and be more honest with yourself. It can aid you with stressful situations as well. You can also use it to track and plan your routine. There are different journaling techniques that can aid you in the process.
-Validate your emotions
Validating your feelings means acknowledging them and being aware of them rather than being judgemental or having a false ideal. Self-validation is a technique from Dialectical Behavior Therapy(DBT) that involves validating and observing your emotions with a neutral perspective.
-Practice gratitude
Start focusing on what you have rather than what you don’t. Find happiness in and appreciate the things and people around you, feel blessed to be alive and live life to the fullest in this world.
-Know when to get help
Despite the difference between stress and anxiety, they share one thing in common. Both can make it difficult for you to function and overwhelm you. If your symptoms interfere with your ability to function or harm multiple areas of your life, such as work, relationships, and family, it is time to seek professional help. Taking a break for your mental health(a mental health day off) or dedicating yourself to recovery is vital if you want to return to your old life quickly. To learn about some of the best online therapy platforms available a click away, click here.
Conclusion
The difference between stress and anxiety is subtle but present, and you can understand both conditions better by studying the differences. Doing so can help you understand your emotions and their complexities better. Emotions are survival or feedback mechanisms for the body or mind that significantly influence our lives. One of these strong emotions is motivation. Lack of motivation can be tiring and harsh and may even lower self-esteem. Here is a secret method by which you can start controlling your dopamine for motivation.
Subscribe to Your Mental Health Pal for more updates about Stress Vs. Anxiety and other mental health-related issues to keep you informed and in the loop.

